As enterprises scale their digital operations, databases become the backbone of business-critical applications—powering analytics, customer platforms, financial systems, and more. However, many organizations still operate without database virtualization, relying on traditional, tightly coupled database environments. This approach often leads to inefficiencies, higher costs, and operational bottlenecks.
What Is Database Virtualization?
Database virtualization is a technology that abstracts database systems from the underlying physical storage and infrastructure. Instead of managing multiple physical copies of databases, enterprises can create virtual database instances or clones that behave like full databases but consume significantly fewer resources.
These virtual databases can be created rapidly and used for:
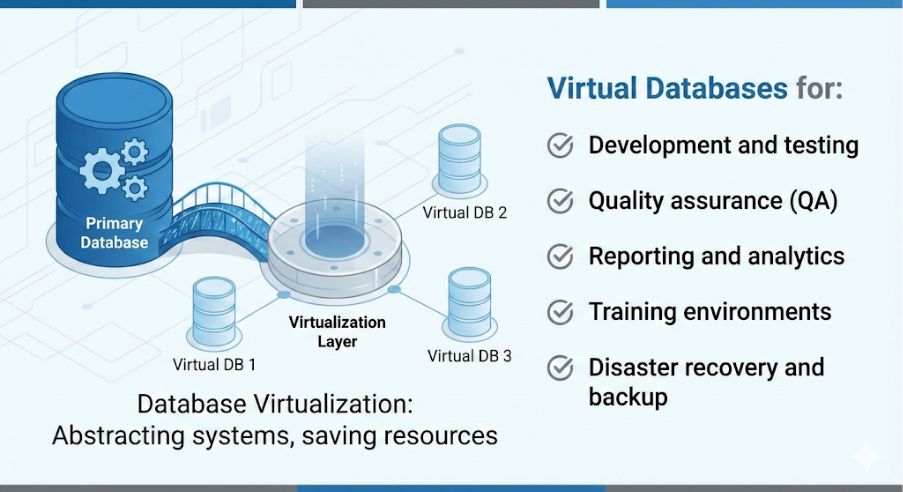
By virtualizing databases, organizations gain flexibility, speed, and cost efficiency without compromising performance or security.
Where Is Database Virtualization Used?
Database virtualization is widely adopted across enterprise environments, including:
- Software development and DevOps – For creating isolated, up-to-date database copies for developers
- Testing and QA teams – For parallel testing without affecting production data
- Business intelligence and analytics – For running reports without impacting live systems
- Enterprises with multiple departments – Where teams need access to the same data without duplication
- Cloud and hybrid infrastructures – To optimize resource usage and scalability
Despite these advantages, many enterprises still operate without data virtualization—and face serious challenges as a result.
Top Challenges Enterprises Face Without Database Virtualization
1. High Infrastructure and Storage Costs
Without database virtualization, enterprises must create full physical copies of databases for development, testing, and backup. This leads to:
- Excessive storage consumption
- Higher hardware and cloud infrastructure costs
- Increased licensing expenses
As data volumes grow, these costs can quickly spiral out of control.
2. Slow Development and Testing Cycles
Traditional database provisioning is time-consuming. Creating a new database environment can take days or even weeks, causing:
- Delays in application development
- Slower release cycles
- Reduced agility in responding to market demands
Without virtualization, teams are forced to wait for database availability instead of innovating.
3. Resource Contention and Performance Issues
When multiple teams share the same physical database:
- Performance degradation is common
- Production systems may be impacted by testing or reporting workloads
- Troubleshooting becomes complex
Lack of isolation increases the risk of downtime and performance bottlenecks.
4. Data Consistency and Versioning Problems
Without virtualized database clones:
- Teams often work on outdated or inconsistent data
- Testing results may not accurately reflect production behavior
- Debugging issues becomes harder due to mismatched data versions
This leads to poor software quality and increased production issues.
5. Increased Risk to Production Data
Sharing production databases across teams increases the likelihood of:
- Accidental data corruption
- Unauthorized changes
- Security and compliance violations
Without virtualization, enterprises struggle to protect sensitive data while still enabling access.
6. Complex Backup and Disaster Recovery
Traditional backup and recovery processes are:
- Storage-intensive
- Time-consuming to restore
- Difficult to test regularly
Without database virtualization, disaster recovery plans are often inefficient and unreliable.
7. Limited Scalability
As enterprises grow, database demands increase. Without virtualization:
- Scaling requires new hardware or database instances
- Provisioning becomes slower and more expensive
- IT teams are overwhelmed managing infrastructure
This lack of scalability restricts business growth.
Pros and Cons of Database Virtualization
Pros of Database Virtualization
- Reduced storage and infrastructure costs
- Faster database provisioning
- Improved development and testing efficiency
- Better isolation and security
- Simplified backup and disaster recovery
- Improved scalability and resource utilization
Cons of Database Virtualization
- Initial setup and learning curve
- Requires proper governance and access controls
- May need specialized tools or expertise
- Performance tuning is necessary for optimal results
Despite these considerations, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks—especially for large and growing enterprises.
Clonetab DBA Acceleration Platform
Clonetab helps enterprises accelerate database operations — powered by automation, AI, and expert DBA intelligence to clone, protect, secure, migrate, and manage databases at scale.
Why Enterprises Should Choose Clonetab for Database Virtualization
To overcome the challenges of operating without database virtualization, enterprises need a reliable, efficient, and easy-to-use solution—and Clonetab fits that role perfectly.
Why Clonetab?
Clonetab is an enterprise-grade database virtualization solution designed to help organizations create secure, space-efficient database clones in minutes.
Key Benefits of Clonetab:
- Rapid Database Cloning
Create virtual database environments instantly without impacting production systems.
- Storage Efficiency
Clonetab uses smart cloning technology to minimize storage usage while maintaining full database functionality.
- Enhanced Security and Compliance
Protect sensitive data with role-based access, masking, and secure isolation.
- Improved DevOps Productivity
Enable developers and testers to work in parallel with consistent, up-to-date data.
- Simplified Backup and Recovery
Quickly restore databases using virtual clones, improving business continuity.
- Enterprise-Ready Scalability
Clonetab scales effortlessly across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments.
Conclusion
Operating without database virtualization exposes enterprises to high costs, slow development cycles, security risks, and scalability limitations. As data volumes and business demands continue to grow, traditional database management approaches are no longer sustainable.
By adopting database virtualization, enterprises can unlock agility, efficiency, and cost savings. Among available solutions, Clonetab stands out as a powerful and practical choice—helping organizations modernize their database strategy while minimizing risk and complexity.
If your enterprise is struggling with database sprawl, slow provisioning, or rising infrastructure costs, it’s time to consider Clonetab as your database virtualization solution.


